The ROI of Curiosity: Quantifying the Business Impact of UX Research
Introduction
The rapid advancement of technology and the proliferation of digital platforms have transformed the way businesses operate and interact externally with their customers and internally with their employees. In an era where users are overwhelmed with options, delivering a superior user experience has become a critical differentiator. Companies that prioritize user-centric design are more likely to succeed, as they can create products and services that resonate deeply with their target audience.
Curiosity is the driving force behind innovation and discovery. In the context of UX Research, it drives researchers to explore into the details of user behaviors and preferences, uncovering insights that can lead to significant improvements in product design and functionality. This article explores how embracing curiosity through UX Research can yield substantial returns on investment (ROI), providing businesses with a competitive edge.
We introduce a UX Research Business Impact Framework, a tool designed to quantify the business value of UX Research activities. By examining seven key dimensions – User Satisfaction, Simplicity, Commitment and Persuasion, User Engagement, Risk Reduction, Efficiency, and Cost and Time Savings – we demonstrate how systematic user research can lead to tangible business benefits. The following Figure depicts the dimensions.
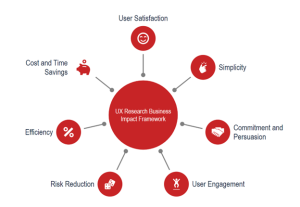
Figure 1: Dimensions of the UX Research Business (own illustration)
The Importance of UX Research
Understanding User Needs
At the heart of UX Research is the systematic study of users to understand their needs, behaviors, motivations, and pain points. By employing various methodologies such as user interviews, surveys, usability testing, facial coding, eye tracking and analytics, researchers gather valuable data on how users interact with products and services. This deep understanding enables businesses to:
- Identify Pain Points: Recognizing areas where users struggle allows for targeted improvements, enhancing the overall user experience.
- Enhance Usability: Insights into user behavior inform design decisions that make products more intuitive and user-friendly.
- Induce User Engagement: Helping design to focus on gain creators resulting in more hedonic and aesthetic user experience
- Inform Feature Development: Understanding what users value most ensures that development efforts focus on features that provide the greatest impact.
Strategic Business Advantages
Integrating UX Research into the product development process offers several strategic benefits that extend beyond product enhancements:
- Cost Reduction: By identifying user needs early, companies can avoid unnecessary features and prevent costly redesigns, optimizing resource allocation.
- Risk Mitigation: Data-driven insights reduce the uncertainty inherent in product development, lowering the risk of market failure.
- Stakeholder Alignment: Presenting evidence-based research fosters alignment among stakeholders, securing buy-in and support for user-centric initiatives.
- Competitive Edge: Delivering superior user experiences differentiates products in a crowded market, attracting and retaining customers.
The UX Research Business Impact Framework
To systematically measure the business impact of UX Research, the UX Research Business Impact Framework encompasses seven key dimensions, each critical to understanding the return on investment. In the following we will define each dimension and provide exemplary metrics for each. The metrics are not mutually exclusive as some can be used to measure aspects of more than one dimension.
1. User Satisfaction
User satisfaction is a fundamental indicator of a product’s success. Applications that fail to meet user expectations often suffer from low adoption rates and high churn. UX Research ensures that products deliver real value by aligning them with user needs and preferences.
Extensive research has shown that satisfied users are more likely to become loyal customers and advocates for the brand. For instance, Reichheld’s Net Promoter Score (NPS) model emphasizes the importance of customer loyalty in driving growth [1]. By measuring user satisfaction through tools like NPS, companies can gauge their performance from the user’s perspective. Other potential metrics are User Experience Quality (UEQ), Voice-of-User (VoU), Conversion Rate, Use Rate, Number of Complaints, Customer Support Tickets or Call Center Traffic.
2. Simplicity
Complex and unintuitive interfaces lead to user frustration, increased support costs, and reduced productivity. UX Research helps simplify designs by understanding how users interact with products and identifying areas of confusion or difficulty.
The System Usability Scale (SUS), is a widely used tool for assessing usability. A higher SUS score indicates a more user-friendly design. Simplifying the user interface not only enhances the user experience but also reduces training costs and time, allowing users to perform tasks more efficiently. Other metrics include Training Time Needed, Training Budget Used, Time on Task, Task Success Rate, Simplicity Score or Ease of Use.
3. User Engagement
User Engagement is the level of positive engagement and reactions to a product. It ranges from the absence of anger and frustration, a good mood up to highly enthusiastic and engaged users. While in B2B product user engagement can secure constant revenue streams e.g. in for users successfully adopting and using B2B SaaS products, in B2C highly engaging products often are the key differentiating factor even resulting in lower customer acquisition costs via word-of-mouth.
Specific metrics can be both subjective metrics such as Product / Brand Liking and objective metrics such as emotional reactions such as Joy, Anger, Frustration, Surprise, Engagement or Valence measured via e.g. facial coding.
4. Commitment and Persuasion
Effective communication of user insights through compelling prototypes and visualizations can secure stakeholder commitment and funding. UX Research provides the empirical evidence needed to persuade stakeholders of the value of user-centric design.
Aligning stakeholders around a common understanding of user needs fosters collaboration and accelerates decision-making. This alignment is crucial for securing resources and support for UX initiatives, ensuring that user insights translate into actionable improvements. An overall metric for this dimension can be the further funding of the UX Research Assets in the company.
5. Risk Reduction
Product development inherently involves uncertainty. Assumptions made without user validation can lead to misguided investments and product failures. UX Research reduces this risk by providing empirical data that informs decision-making.
By involving users early in the development process, companies can validate concepts, identify potential issues, and adjust strategies accordingly. This proactive approach minimizes the likelihood of costly post-launch fixes and enhances the likelihood of market success. Potential metrics for this dimension encompass Amount of Available / Analyzed Data Points, Data Analytics Implemented (binary metric: YES / NO), VoE Implemented (binary metric: YES / NO), Number of Research / Design Iterations, User Value Known (binary metric: YES / NO), User Group Knowledge and Team Risk / Uncertainty Perception.
6. Efficiency
Inefficient user interfaces and workflows decrease productivity and increase operational costs. UX Research identifies bottlenecks and areas where users expend unnecessary effort, allowing for optimization of processes.
Improved efficiency benefits both users and the organization. Users can complete tasks more quickly and with less frustration, while the organization benefits from increased productivity and reduced support costs. Time-on-task studies are instrumental in quantifying efficiency gains. Furthermore, companies can measure metrics such as Time on Site, Task Success Rate, Number of Clicks or the Simplicity Score.
7. Cost and Time Savings
By focusing development efforts on validated user needs, companies can reduce time-to-market and avoid the expenses associated with unnecessary features or redesigns. UX Research ensures that resources are allocated effectively, maximizing return on investment.
Time-to-market is a critical factor in gaining competitive advantage. Products that reach the market faster can capture market share and respond to user needs promptly. UX Research streamlines the development process by clarifying requirements and reducing rework [2]. Researchers can also use metrics such as Time-to-Decision, Hrs. Spend on Data Interpretation, Number of Rollout-Delays, Decision Meeting Lengths, Number of UX Re-Designs, Component Re-Use or Front-End Maturity.
Implementing the Framework
To effectively apply the UX Research Business Impact Framework, organizations should undertake a structured approach:
- Define Objectives: Clearly articulate what the UX Research aims to achieve, aligning it with broader business goals. This clarity ensures that efforts are focused and measurable.
- Select Appropriate Metrics: Choose KPIs that are relevant to the specific context and objectives. Metrics should be quantifiable, reliable, and able to capture changes over time.
- Establish Baselines: Determine current performance levels to provide a reference point for measuring improvements. Baselines enable organizations to quantify the impact of UX interventions.
- Collect Data: Employ robust research methodologies to gather both quantitative and qualitative data. Diverse data sources enrich insights and enhance the validity of findings.
- Analyze Results: Interpret data to identify trends, patterns, and areas for improvement. Analysis should be rigorous and consider both statistical significance and practical relevance.
- Report Findings: Communicate results to stakeholders in a clear and compelling manner. Effective reporting fosters understanding, drives action, and reinforces the value of UX Research.
The ROI of UX Research
Quantifying the return on investment in UX Research involves linking improvements in user experience to tangible business outcomes. The benefits are multifaceted:
- Increased Revenue: Enhanced user satisfaction leads to higher conversion rates, repeat purchases, and customer loyalty, directly impacting revenue.
- Cost Efficiency: By avoiding unnecessary features and reducing redesigns, companies save on development and operational costs.
- Market Positioning: Products that offer superior user experiences stand out in the market, attracting new customers and retaining existing ones.
- Innovation: UX Research uncovers unmet user needs, fueling innovation and the development of new products or services.
The following table shows an exemplary calculation of a UX Research Project. For an internal sales platform, the feature backlog was overwhelming and stakeholder alignment on feature priorization was low. In the research project, a Senior UX Researcher focused on the user-centric exploration of feature elimination and could – besides ranking the other features in the backlog – entirely eliminate 12 of 40 proposed feature requests due to low user value. This resulted in cost savings of EUR 120.000 against UX research costs of EUR 28.000 resulting in a ROI of 328%. This example shows that UX research not only is useful for determining “what to do” but also to avoid non-user centric developments, i.e. deciding “what not to do”.
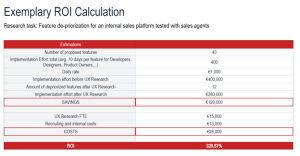
Table 1: Quantifying the Business Impact of UX Research
These figures underscore the significant impact that UX Research can have on a company’s bottom line.
Challenges and Best Practices
Common Challenges
While the benefits of UX Research are clear, organizations may face challenges in implementation:
- Resource Constraints: Limited budgets and time pressures can hinder comprehensive research efforts. Balancing immediate demands with long-term benefits requires strategic planning.
- Cultural Resistance: Organizational resistance to change or skepticism about the value of UX Research can hinder adoption. Overcoming this requires education and demonstration of value.
- Data Management: Handling large volumes of data and translating insights into action can be complex. Investing in skilled researchers and appropriate tools is essential.
Best Practices
To maximize the impact of UX Research, organizations should consider the following best practices:
- Integrate UX Research Early: Incorporate user research from the project’s inception to influence design decisions proactively.
- Foster a User-Centric Culture: Encourage a culture that values user insights across all levels of the organization.
- Prioritize Continuous Improvement: Treat UX Research as an ongoing process, continually refining products based on user feedback.
- Facilitate Cross-Functional Collaboration: Promote collaboration between UX researchers, designers, developers, and stakeholders to ensure alignment and effective implementation.
Future Perspectives
As technology continues to evolve, UX Research will adapt to address new challenges and opportunities:
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: Leveraging AI and ML can enhance data analysis, uncovering deeper patterns and predictions about user behavior.
- Personalization: Increasingly, users expect personalized experiences. UX Research will play a critical role in understanding individual preferences and tailoring experiences accordingly.
- Ethical Considerations: Ensuring privacy and ethical data handling is paramount. UX researchers must navigate the balance between gathering insights and respecting user rights.
- Global and Cross-Cultural Research: As businesses operate on a global scale, understanding cultural differences becomes essential. UX Research must account for diverse user groups to create inclusive designs.
Conclusion
Embracing curiosity through UX Research offers a powerful avenue for businesses to enhance their products and services, ultimately leading to significant returns on investment. By systematically investigating user needs and behaviors, organizations can create experiences that not only meet but exceed user expectations.
The UX Research Business Impact Framework provides a structured approach to quantify this impact, linking UX activities directly to business outcomes. It underscores that investing in UX Research is not merely a cost but a strategic initiative that yields measurable benefits.
In a market characterized by rapid change and intense competition, organizations that let curiosity guide their product development are better positioned to innovate, satisfy customers, and achieve sustainable growth. By recognizing and harnessing the ROI of UX Research, businesses can unlock new levels of success and competitive advantage.
References
1. Reichheld, F. F. (2003). The One Number You Need to Grow. Harvard Business Review, 81(12), 46–55.
2. Cooper, A., Reimann, R., Cronin, D., & Noessel, C. (2014). About Face: The Essentials of Interaction Design (4th ed.). John Wiley & Sons.




Um einen Kommentar zu hinterlassen müssen sie Autor sein, oder mit Ihrem LinkedIn Account eingeloggt sein.